Home / Heart Arrhythmia Specialist
What is Arrhythmia?
An arrhythmia is an abnormal heartbeat either too fast, too slow, or an irregular heartbeat. Frequently an arrhythmia may be asymptomatic but at times may present as a racing heartbeat or fluttering, a skipping heartbeat or “pause”, and even at times dizziness. Some arrhythmias are potentially dangerous and an evaluation including an electrocardiogram and a 24 hour Holter monitor can be useful in diagnosing what type of arrhythmia is present.
Arrhythmia is a heart condition that causes your heart to beat too fast, too slow or with an irregular pattern. This abnormality in your heart rhythm can sometimes turn into a heart condition like coronary heart disease, conductive tissue disease or heart valve disease. In serious cases, arrhythmia is also associated with myocardial infarctions or a stroke.
Arrhythmia often has no symptoms. You may only discover your irregular heartbeat during a routine checkup with the cardiologist at the Cardiology Center in Manhattan. You might have Arrhythmia
if you experience any symptoms associated with heart disease, such as:
- Chest pain
- Trouble breathing
- Syncope or lightheadedness
- Unexplained sweating
- Heart palpitations, causing a racing, pounding or fluttering feeling
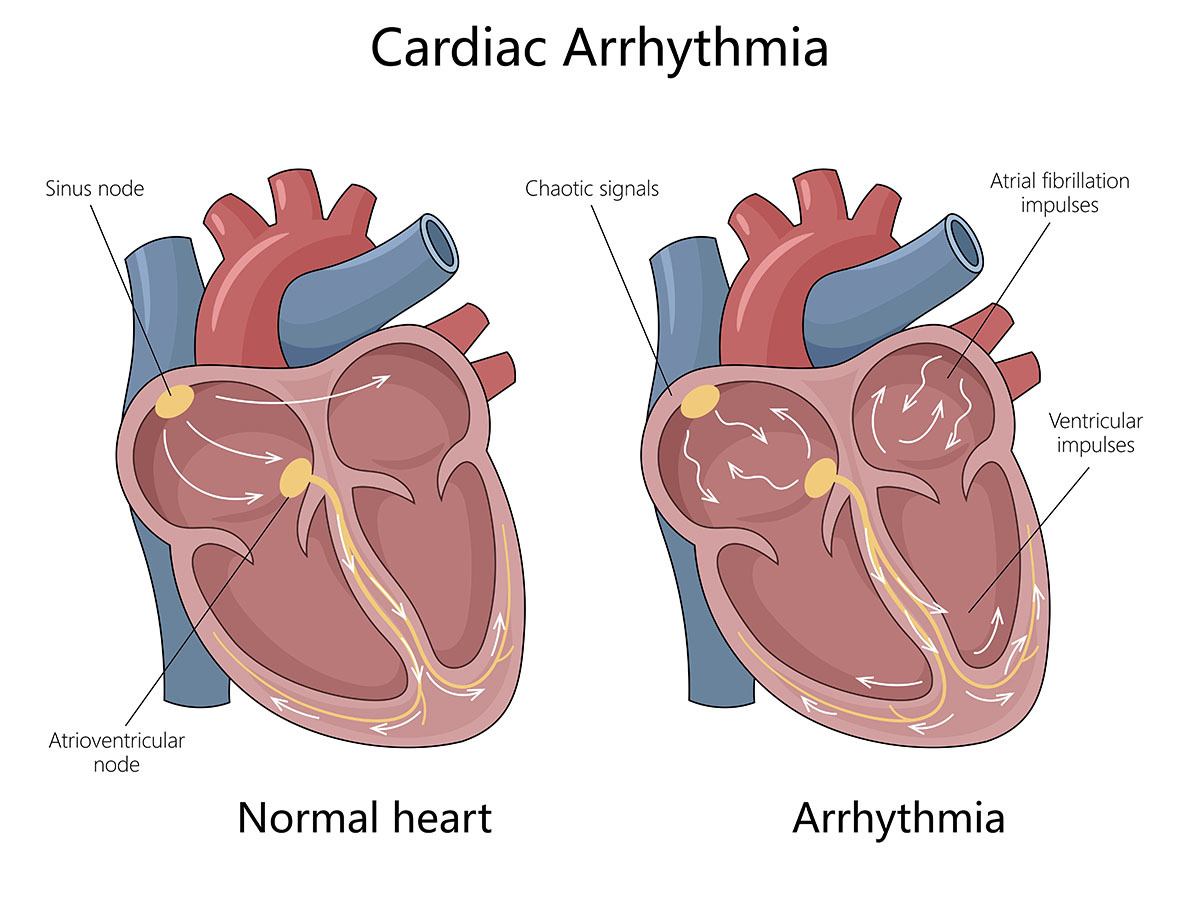
Recognizing Abnormal Heartbeat Patterns
One in every four Americans over the age of 40 suffers from arrhythmia. If your heart rate is slower than 60 beats per minute, the condition is called bradyarrhythmia. If your heart beats faster than 100 beats per minute, you are suffering from tachyarrhythmia. The electrical impulses are usually disoriented in one of three places:
- The atria or upper chamber of your heart
- The ventricles or lower chamber of your heart
- An area in between, your accessory pathways
Read more: The Difference Between Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
I have known Dr. Reisman for many years. My first experience with him was through a friend’s referral. A family situation came along where we needed a cardiologist, a great one. I am very thankful that I was referred to Dr. Reisman. He is a true leader in his field; very caring for his patients and he will go out of his way to help anyone. Dr. Reisman is very approachable and friendly. His office staffs are very friendly. After attending to my family situation I too was in need of a cardiologist for stress testing – I have been to the Wall Street & Upper East Side location – one close to work and one close to home. Again, my experience was 100% positive. If you are looking for a cardiologist don’t look any further. ~ ZocDoc
Types of Arrhythmia
Symptoms and conditions that may require arrhythmia treatment for your heart include:
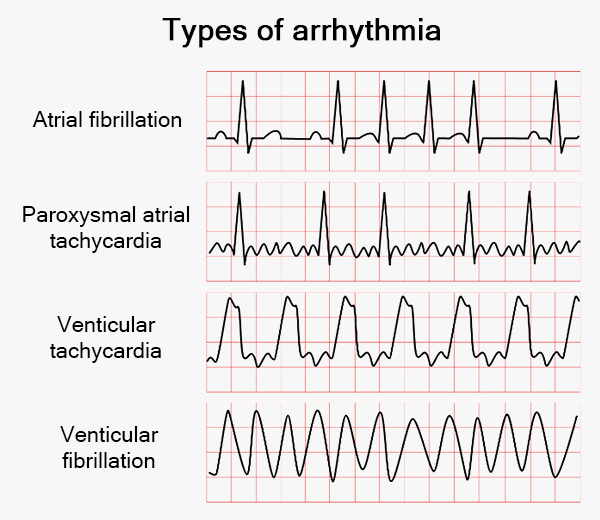
- Atrial fibrillation. This condition puts nearly 2.7 million Americans at risk for sudden cardiac death and stroke. Atrial fibrillation causes irregular electrical impulses, leading to blood clots and other fatal coronary diseases.
- Atrial flutter. When your heart beats fast, but with an even rhythm, it creates weak contractions of the atria. This can compromise your heart, potentially leading to a stroke.
- Heart block. This condition is characterized by how slowly the electrical impulses move from your atria to your ventricles.
- Long QT syndrome. If your heart starts beating fast and chaotically, you can faint or have a seizure. If you don’t get treatment, it can be fatal.
- Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. This condition develops at any age. It’s often misdiagnosed as a panic attack.
- Sick sinus syndrome. When your heart’s natural pacemaker is compromised, it results in a slow heart rate. In some cases, your heart rate fluctuates between a slow rate and a rapid rate.
- Ventricular tachycardia. With this disease, you require immediate medical assistance, as it prevents your ventricles from pumping sufficient blood throughout your body.
- Ventricular fibrillation. An extreme version of ventricular tachycardia, this is often fatal if your heart rhythm isn’t restored to normal within minutes. Nearly 85 percent of sudden cardiac deaths are linked to this illness.
- Ventricular ectopic. Your heart beats prematurely, followed by a significant pause. The beat after the pause is usually stronger, making it feel like your heart’s fluttering.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. A birth defect that doesn’t show symptoms until you’re an adult, this abnormal electrical connection occurs in your accessory pathways. It disrupts your normal heart rate.
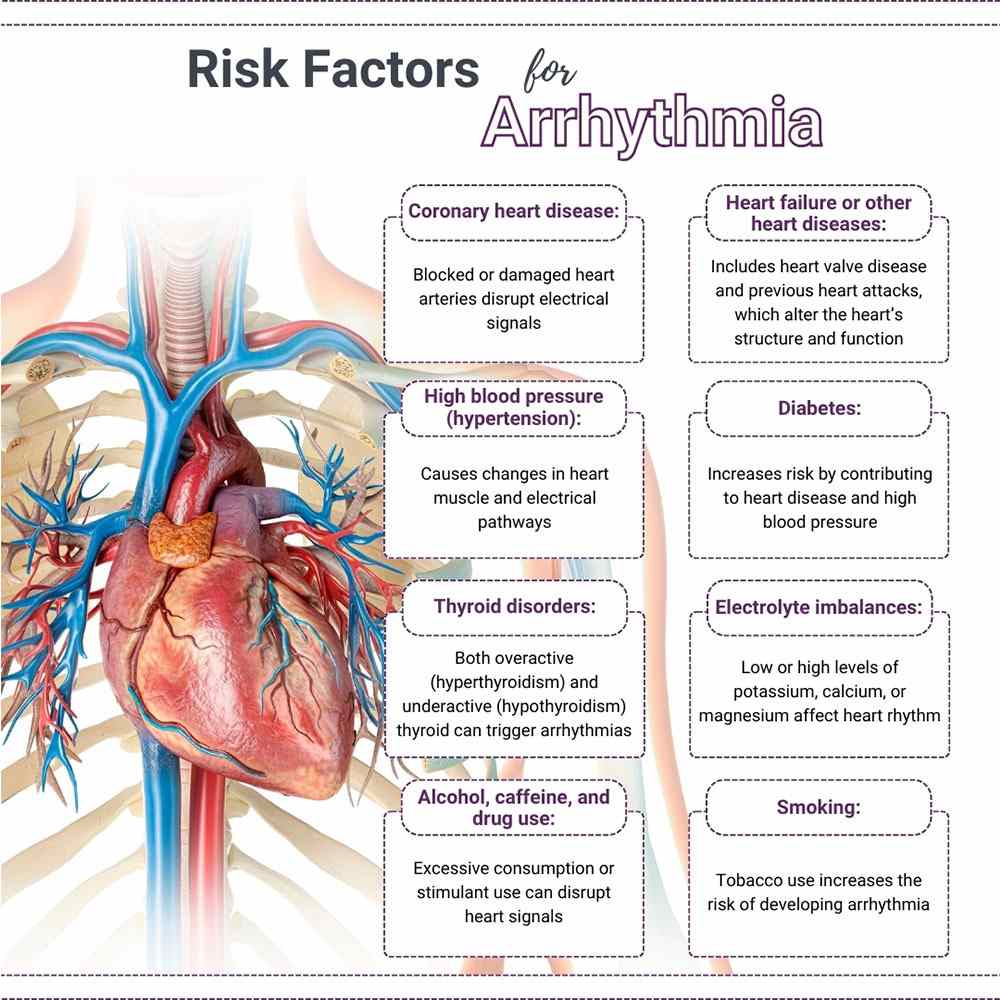
Underlying Risk Factors for Arrhythmia
Determining the risks of developing an irregular heartbeat is a specialty of your arrhythmia specialist. Age, for example, is a factor, as people over the age of 40 are at a higher risk. Race is another risk factor, as Caucasians are more inclined to get arrhythmia, especially atrial fibrillation.
Other risk factors for developing an irregular heartbeat include:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Sleep apnea
- Genetics
- Obesity
- Stress
- Caffeine and alcohol
- Smoking
- Thyroid hormone imbalance
- Over-the-counter antibiotics
- Low levels of potassium, magnesium or calcium
- Medication for high blood pressure, depression or psychosis
Cardiac Tests for Arrhythmia in NYC
To get the right treatment for your condition, your cardiology doctor conducts a thorough examination in the cardiovascular center. You may also have to undergo tests to measure your heartbeat, which points your cardiologist toward a particular arrhythmia treatment for you. Your tests may include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG). Using electrical impulses, this test shows how your heart is functioning.
- Heart monitors. This is a device you wear for a set period of time. It records the heartbeats while you’re physically active.
- Like an ECG, except an echocardiogram uses ultrasound to create a live image of your heart.
- Stress test. You walk or run on a treadmill. Your heart is continuously monitored to determine if anything happens to it under stress.
Treating Your Heart
For bradycardia, an artificial pacemaker may be the best solution in some instances, as it safely monitors your heartbeats and sends electrical impulses to stimulate a normal heartbeat when your heart rate slows.
If you have tachycardia, your best arrhythmia specialist in NYC may recommend:
- Vagal maneuvers. Hold your breath and strain, dunk your face in ice water or cough to jolt the vagus nerves and slow down your heart rate.
- A shock of electricity gets your heart rhythm back to normal.
- Catheter ablation. This technique uses electrodes on a catheter tip, inserted inside the blood vessels of your heart. It ablates the small part of your heart that’s causing arrhythmia.
- These may include blood thinners, calcium channel blockers, beta blockers and antiarrhythmics.
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). This is a device that monitors your heart rate and shocks the heart in case of irregular and dangerous heartbeats.
Get checked up for irregular heartbeat. Contact the New York Cardiac Diagnostic Center for an evaluation and treatment of arrhythmia in NYC. If you have any questions for the best in class Manhattan cardiologist or would like to schedule a consultation or appointment please feel free to contact Dr. Steven Reisman of the Manhattan Heart Testing and Cardiology Center and indicate which Manhattan office (Upper East Side, Midtown Cardiologist, or Wall Street / Financial District) for an arrhythmia treatment consultation.

Dr. Steven Reisman is an internationally recognized cardiologist and heart specialist. He is a member of the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and a founding member of the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology.
Dr. Reisman has presented original research findings for the early detection of "high risk" heart disease and severe coronary artery disease at the annual meetings of both the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association. Dr. Reisman was part of a group of doctors with the Food and Drug Administration who evaluated the dipyridamole thallium testing technique before the FDA approved it.
Dr. Steven Reisman's academic appointments include Assistant Professor of Medicine at the University of California and Assistant Professor at SUNY. Hospital appointments include the Director of Nuclear Cardiology at the Long Island College Hospital.


